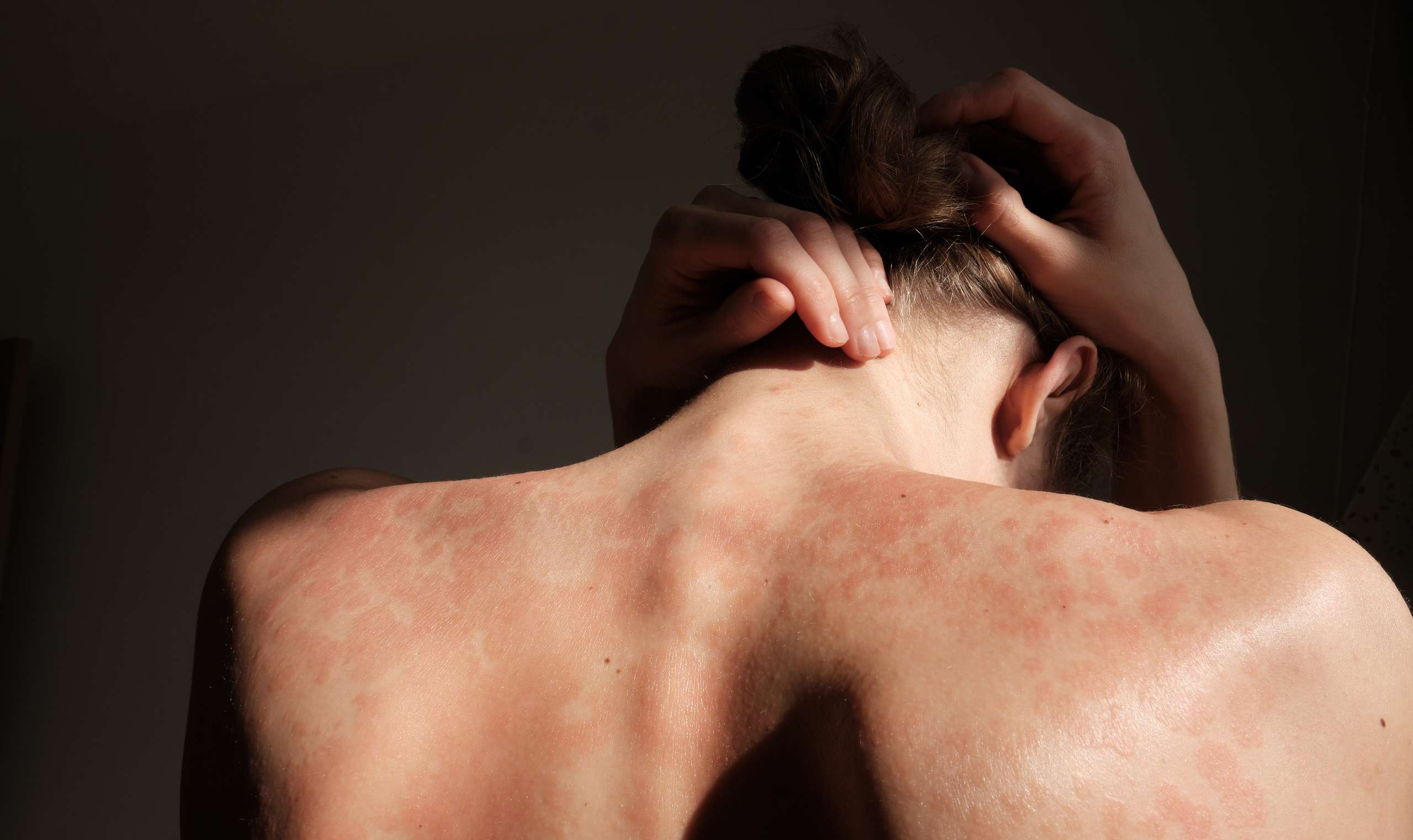
At DermDox, we offer specialized and compassionate care for individuals dealing with psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by red, inflamed patches of skin covered with silvery scales. Our expert dermatologists at DermDox are dedicated to providing comprehensive psoriasis treatment services, tailored to each patient’s unique needs and severity of the condition. We understand the physical and emotional challenges psoriasis can bring, and our team is committed to helping our patients manage their symptoms effectively. Through a combination of advanced therapies, topical treatments, and systemic medications, we aim to reduce inflammation, alleviate discomfort, and improve the overall quality of life for our patients.
In addition to medical interventions, DermDox places a strong emphasis on patient education and support. We believe that informed patients are better equipped to manage their condition. Our dermatologists work closely with each individual, providing personalized advice on lifestyle modifications, stress management techniques, and proper skincare routines to minimize flare-ups and promote long-term skin health. By offering specialized psoriasis treatment services, DermDox is dedicated to helping patients achieve clearer, healthier skin, allowing them to regain confidence and embrace life to the fullest.
Frequently Asked Questions
The exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, immune system, and environmental factors. Psoriasis is considered an autoimmune disease, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to an accelerated skin cell turnover. This rapid growth of skin cells results in the characteristic symptoms of psoriasis, including red, inflamed patches covered with silvery scales.
Genetics play a significant role in psoriasis. If one or both parents have psoriasis, the likelihood of developing the condition increases. However, not everyone with a genetic predisposition will develop psoriasis, indicating that environmental factors also play a crucial role in triggering the disease.
Various environmental factors can trigger the onset or exacerbation of psoriasis symptoms. Common triggers include stress, skin injuries (such as cuts, burns, or insect bites), infections (such as streptococcal throat infections), certain medications (such as beta-blockers and lithium), smoking, and heavy alcohol consumption. Additionally, changes in weather, hormonal imbalances, and certain dietary factors may influence psoriasis symptoms in some individuals.
It’s important to note that psoriasis triggers can vary widely from person to person, and what affects one individual may not affect another.
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that can vary in severity and presentation, but common signs and symptoms of psoriasis include:
Red, Inflamed Skin: Psoriasis often appears as red or pink patches of skin that are inflamed and may be covered with silvery-white scales.
Thickened Skin: Over time, the affected skin areas may become thickened and develop a rough, scaly texture due to the rapid growth of skin cells.
Silvery Scales: The patches of psoriasis are often covered with silvery-white scales, which are a result of the excessive skin cell turnover.
Itching and Burning: Psoriasis lesions can be itchy and may cause a burning sensation, leading to discomfort for individuals with the condition.
Dry or Cracked Skin: The affected skin areas may become dry and prone to cracking, especially if left untreated.
Nail Changes: Psoriasis can affect the nails, causing changes such as pitting (small dents or depressions), discoloration, thickening, or separation of the nail from the nail bed.
Joint Pain: In some cases, psoriasis can lead to a form of arthritis called psoriatic arthritis, causing joint pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Lesions on Scalp: Psoriasis can occur on the scalp, leading to red patches covered with scales and sometimes extending beyond the hairline onto the forehead, neck, and behind the ears.
Lesions in Skin Folds: Inverse psoriasis appears as smooth, red lesions in skin folds, such as under the breasts, in the armpits, or in the groin area.
While there is no definitive cure for psoriasis, there are various treatments that can help manage the condition and alleviate symptoms. The effectiveness of these treatments can vary from person to person, and what works quickly for one individual may not have the same rapid effect for another. It’s essential to consult a dermatologist to determine the most appropriate and effective treatment plan tailored to your specific condition. Here are some methods that might help manage psoriasis symptoms relatively quickly:
Topical Treatments: Corticosteroid creams or ointments can help reduce inflammation and itching, providing relief for mild to moderate psoriasis symptoms. Non-steroidal topical treatments, such as calcineurin inhibitors, can also be prescribed.
Moisturizers: Keeping the affected skin well-moisturized with emollients or thick creams can help soothe dryness and reduce scaling.
Oral Medications: For more severe cases, oral medications, such as cyclosporine or methotrexate, can be prescribed to suppress the immune system and reduce psoriasis symptoms. Biologic drugs, administered via injection or infusion, target specific parts of the immune system and can lead to rapid improvement in some cases.
Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers, such as stress, certain foods, alcohol, or specific medications, can prevent flare-ups and promote quick relief from symptoms.
Wet Wrap Therapy: Applying wet bandages or wraps over moisturized skin, under medical supervision, can provide intensive hydration and relief for psoriasis symptoms.
It’s important to note that while these treatments can provide quick relief, long-term management of psoriasis often involves a combination of treatments and ongoing care to maintain symptom control and prevent flare-ups.
If psoriasis is left untreated or inadequately managed, it can lead to several complications and adversely affect both physical and emotional well-being. Some potential consequences of untreated psoriasis include:
Increased Severity: Psoriasis symptoms may worsen over time, leading to larger, more inflamed, and more widespread patches of affected skin. Severe psoriasis can cover a significant portion of the body, causing considerable discomfort.
Physical Discomfort: Psoriasis can be itchy, painful, and prone to cracking and bleeding, leading to physical discomfort and a decreased quality of life.
Psychological Impact: Psoriasis is not just a skin condition; it can have a significant impact on a person’s mental health. Individuals with untreated psoriasis may experience anxiety, depression, and a decreased self-esteem due to the visible nature of the condition.
Psoriatic Arthritis: About 30% of people with psoriasis develop psoriatic arthritis, a condition that causes joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. If left untreated, psoriatic arthritis can lead to joint damage and disability.
Increased Risk of Other Health Conditions: Psoriasis has been associated with an increased risk of developing other health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain autoimmune disorders.
Impaired Quality of Life: Due to the physical discomfort, emotional distress, and social stigma associated with psoriasis, individuals with untreated psoriasis may experience a reduced overall quality of life and limitations in daily activities.
Chronic Inflammation: Psoriasis is linked to chronic inflammation in the body, which may contribute to various systemic health issues if left unaddressed.
It’s crucial to seek medical attention if you suspect you have psoriasis or are experiencing symptoms.